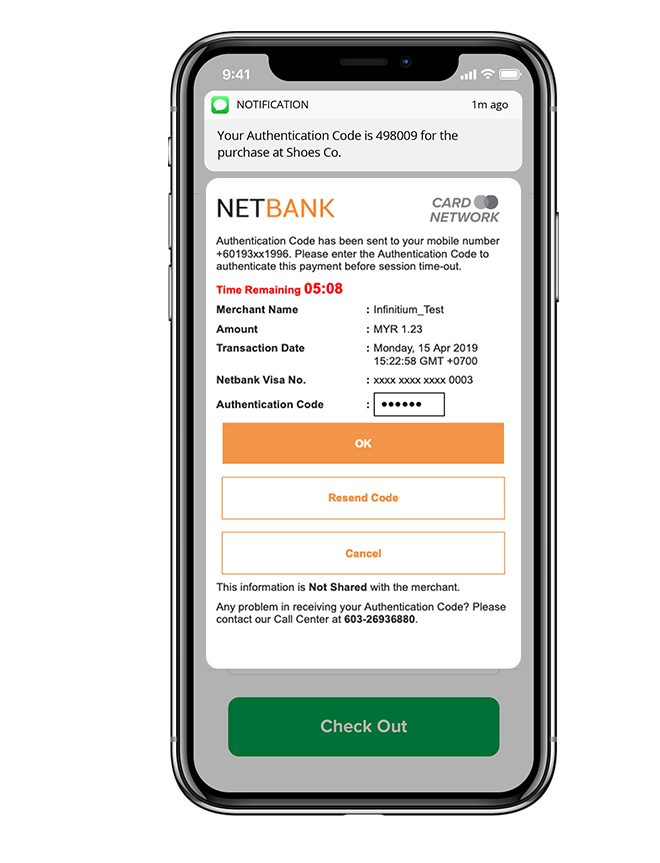
To address these challenges, Infinitium took an innovative approach in the late 2000s by implementing Dynamic 2-Factor Authentication with One-Time-Passcode (OTP) on 3DS transactions. Many Issuing banks saw an immediate uplift in the success rate as their cardholders no longer need to remember complicated passwords when performing online transactions.
While OTP had its glorious days since its introduction, another challenge surfaced as more transactions migrated from PC browsers to Smartphone browsers and in-app purchases. Not only the shopping device is now the same device receiving the OTP, the look-and-feel varies widely with different models of the mobile devices. As payments methods evolved, online payments using the 3DS 1.0 protocol proved to be limiting in user experience amidst an increasingly fast-paced e-commerce environment.
To keep up with the changes, EMVCo released EMV 3DS (also known as 3DS 2.0), an enhanced protocol standard that aims to address these issues by utilising payment behavioural data for Risk-Based Authentication and security purposes, as well as providing multi-channel and multi-device support through various form factors and use cases. This will lead to reduced user friction and increased transaction approvals for cardholders, resulting in a more e-commerce friendly environment for merchants and consumers.
3-D Secure & IMS 2.0
The Access Control Server (ACS) is a key 3DS component in the Issuing domain that reduces the chances for fraud. Upon receiving an Authentication Request, the ACS is responsible for authenticating the cardholder’s transaction – either through a challenge flow or a frictionless flow.
At the point of card transaction from the Issuing Domain, the ACS will challenge to acquire information about the cardholder in the form of 2-Factor Authentication (2FA) with One-Time-Passcode (OTP), Biometrics or Risk-Based Authentication (RBA). The received data will go through a series of processes that occurs within a few seconds to minutes between the Issuing, Acquiring and Interoperability domains to either approve or deny the cardholder’s transaction.
Infinitium’s IMS 2.0 is the software application specifically designed to facilitate the Issuer Domain with its ACS functions. By taking a duo-compatibility approach with IMS 2.0, Infinitium’s application can support both 3DS 1.0 and EMV 3DS (2.0) protocol specifications on a single application. Thus, IMS 2.0 is capable of supporting banks who have yet to adopt the newer specification of EMV 3DS (2.0), allowing them to continue serving their cardholders until 3DS 1.0 is phased out.
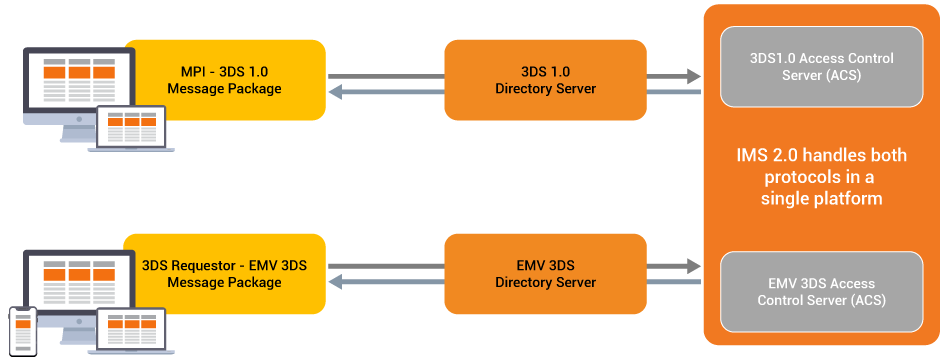
Apart from that, Infinitium’s IMS 2.0 is capable of handling heavy loads of website traffic with its High Availability and Load Balancing features. IMS 2.0 is in compliance with the latest specification of EMV 3DS 2.2.0 and has been certified with the following payment schemes and their respective 3DS programs: American Express SafeKey, Japan Credit Bureau (JCB) JSecure, MasterCard ID Check, MyDebit Secure, UnionPay, and Visa Secure. In addition, IMS 2.0 is also certified with the standards of PCI Security Standards Council.
Challenge or Frictionless Flow for Cardholder Authentication
Under the EMV 3DS (2.0) protocol specification, a cardholder may experience either a challenge flow or a frictionless flow. One of the common use case of challenge flow is the use of One-Time-Passcode (OTP). During the authentication process, an OTP will be generated by the ACS and sent to the cardholder’s pre-registered mobile phone. Cardholder enters this OTP into the authentication challenge page for further validation by the ACS.
Besides OTP, Infinitium has also built on the successful IMS platform to offer other authentication challenge options such as the use of native biometrics capabilities of the devices in the form of fingerprint, face recognition and more, as a 3DS Out-Of-Band (OOB) authentication method for the transaction.
Infinitium’s IMS 2.0 is a comprehensive ACS application that could be associated with a risk assessment engine. Through this risk-engine, an authentication request may be assessed for its riskiness and if the risk is deemed low, Issuer may provide the cardholder a smoother checkout experience without an OTP or a biometrics challenge. This is known as Risk-Based Authentication (RBA). Such frictionless experience helps in reducing the chances for unintentional shopping cart abandonment.